Table of Contents
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become one of the most transformative technologies of the 21st century, revolutionizing industries, processes, and the way businesses operate. One of the most exciting and rapidly evolving areas of AI is the development of AI agents. These intelligent systems, capable of autonomous decision-making and problem-solving, are rapidly changing the landscape of business operations. In this blog, we will explore what AI agents are, how they work, and the potential they hold for businesses in various industries.
What are AI Agents?
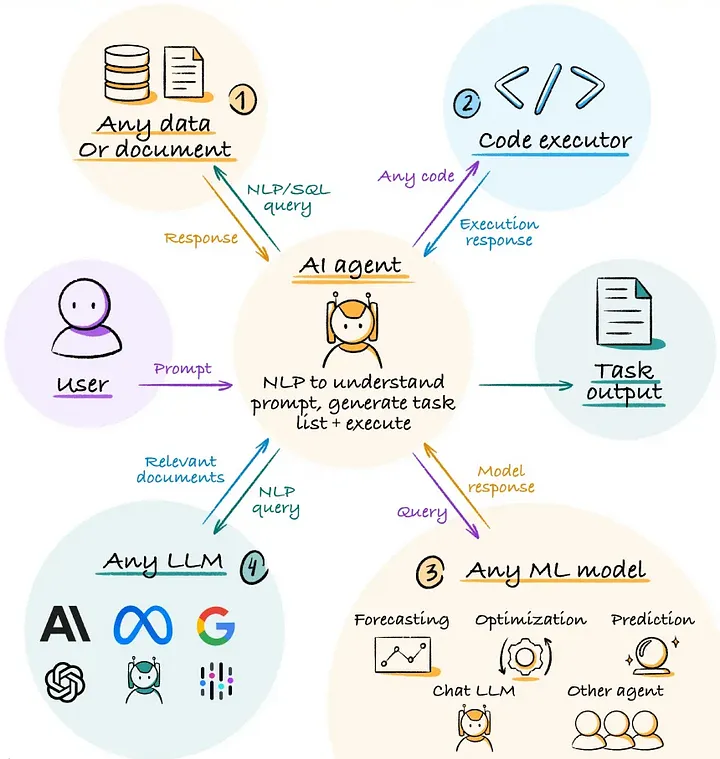
At their core, AI agents are systems designed to act autonomously to achieve a set goal or solve a problem. Unlike traditional software that follows pre-programmed instructions, AI agents have the ability to learn, adapt, and make decisions based on the data they receive.
These agents can range from simple chatbots that handle customer service requests to sophisticated autonomous systems used in industries like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing. AI agents typically rely on machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and other AI technologies to interpret and respond to their environment.
The key difference between AI agents and traditional software is their ability to learn and evolve. They are not just reactive to inputs—they can proactively anticipate needs, make complex decisions, and continuously improve over time.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents can be classified based on their capabilities, from basic reactive agents to highly advanced autonomous systems. Here are a few common types:
-
Reactive Agents: These agents respond to stimuli or inputs based on predefined rules or patterns. They do not store information or learn from past actions. A simple chatbot is an example of a reactive agent.
-
Deliberative Agents: These AI agents have a model of the world and can plan their actions by reasoning through different possibilities. They are more advanced and can perform tasks like route planning or resource allocation.
-
Autonomous Agents: These agents operate independently and are capable of learning from their environment and experiences. Autonomous vehicles, such as self-driving cars, are a prime example of this type of AI agent.
-
Collaborative Agents: These agents work in teams with other agents or humans to achieve a common goal. They are often used in environments where teamwork is required, such as in virtual assistants or customer service.
How AI Agents Work
AI agents work by gathering information from their environment, processing that information, and making decisions to achieve their assigned objectives. The process typically involves several key steps:
-
Perception: The AI agent collects data from its environment using sensors, cameras, microphones, or other input devices. This data is processed using machine learning algorithms, which help the agent understand its surroundings.
-
Reasoning and Decision-Making: Once the agent has collected information, it needs to analyze it and make decisions. This is where AI comes into play. Using algorithms, neural networks, or other AI methods, the agent reasons about the best course of action to take based on its objective.
-
Action: After making a decision, the AI agent executes its action. This could involve interacting with humans (e.g., a virtual assistant answering a query), controlling a device (e.g., a robot assembling products), or even initiating a new process.
-
Learning: One of the most powerful aspects of AI agents is their ability to learn from experience. Machine learning techniques allow agents to improve over time, becoming more efficient and effective at performing their tasks.
The Benefits of AI Agents for Businesses
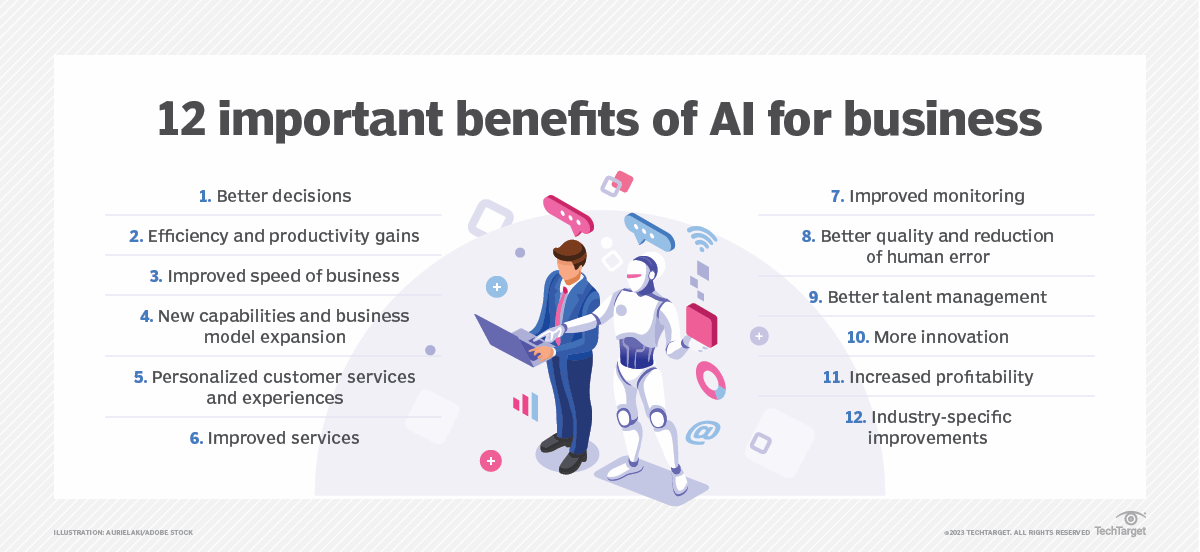
The rise of AI agents offers numerous benefits for businesses, ranging from cost savings and improved efficiency to new business opportunities. Here are some ways AI agents can positively impact businesses:
-
Enhanced Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide 24/7 customer support, answering questions, resolving issues, and guiding customers through processes. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also reduces the need for human intervention in routine inquiries.
-
Automation of Repetitive Tasks: AI agents can automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, such as data entry, inventory management, or financial reporting. This frees up employees to focus on more strategic and creative aspects of their work.
-
Improved Decision-Making: AI agents can analyze large volumes of data and generate insights that help businesses make better decisions. Whether it's predicting customer behavior, optimizing supply chains, or determining the best marketing strategies, AI agents can provide actionable intelligence.
-
Cost Efficiency: By automating tasks and processes, businesses can reduce labor costs and increase operational efficiency. AI agents can work around the clock without the need for breaks or downtime, leading to significant cost savings in the long run.
-
Personalization: AI agents can deliver personalized experiences to customers by analyzing individual preferences and behaviors. For instance, AI-powered recommendation systems, like those used by Netflix or Amazon, can suggest products or content based on a user's past activity, increasing engagement and sales.
Real-World Applications of AI Agents
AI agents are already being used in a variety of industries to drive innovation and improve business outcomes. Here are a few notable examples:
-
Healthcare: AI agents are being used to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases, analyzing medical images, and providing treatment recommendations. Virtual health assistants are also helping patients manage their health conditions by providing reminders, answering questions, and tracking progress.
-
Finance: In the financial sector, AI agents are being used to analyze market trends, detect fraud, and assist in making investment decisions. Robo-advisors, for example, provide personalized financial advice based on an individual's goals and risk tolerance.
-
Retail: AI agents are transforming the retail industry by helping businesses optimize inventory management, personalize shopping experiences, and improve customer service. Virtual shopping assistants can guide customers through product selections, while AI-powered supply chain agents can predict demand and optimize stock levels.
-
Manufacturing: In manufacturing, AI agents are used to control robots that assemble products, monitor production lines for quality assurance, and even predict equipment failures before they happen. This increases productivity and minimizes downtime.
Challenges and Considerations
While AI agents hold immense potential, there are still challenges and considerations that businesses must address when implementing them:
-
Data Privacy and Security: AI agents often require access to sensitive data, which raises concerns about privacy and security. Businesses must ensure that their AI agents comply with data protection regulations and that data is handled securely.
-
Ethical Concerns: As AI agents become more autonomous, there are ethical concerns regarding their decision-making, particularly in industries like healthcare and finance. It's crucial to ensure that AI agents operate in a transparent and ethical manner.
-
Job Displacement: The automation of tasks by AI agents could lead to job displacement in some industries. While AI can increase efficiency, businesses must also focus on retraining employees and creating new roles that complement AI technology.
Conclusion: The Future of AI Agents in Business
AI agents are poised to transform the business landscape in profound ways. From enhancing customer service to driving innovation in product development and operations, these intelligent systems have the potential to create new business models, streamline processes, and unlock opportunities that were previously unimaginable. However, businesses must be mindful of the challenges that come with AI adoption, such as data privacy, ethical considerations, and job displacement.
As technology continues to evolve, the future of AI agents looks incredibly promising. The businesses that embrace AI agents today will be the ones leading the way into a new era of efficiency, innovation, and success.